
Unauthorised access and theft of sensitive customer or business data, such as payment details and personal information, is referred to as an e-commerce data breach. Such incidents severely impact online businesses by undermining trust. Trust is the foundational currency of the digital marketplace.
The magnitude of the threat is staggering. In 2019, data breaches exposed 15 billion records, entailing severe financial consequences. The average cost of such a breach is approximately $4.44 million in 2025 [IBM Report]. Maintaining client trust, guaranteeing revenue streams, and adhering to a complex web of regulations, such as GDPR, CCPA, and PCI DSS, all depend on an e-commerce company protecting its digital assets. This article is the best resource for understanding, preventing, and mitigating e-commerce data breaches.
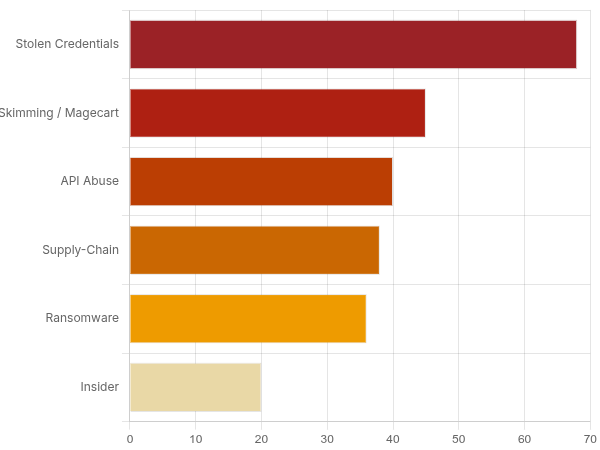
Real-World Impact of E-commerce Data Breaches
The consequences of a data breach extend far beyond immediate financial costs, inflicting long-term damage on a brand’s reputation and legal standing. Below is a concise overview of the most significant data-security incidents reported by Verizon since 2020, illustrating the escalating financial and reputational risks organizations now face.
High-Profile Breaches
- PowerSchool (Dec-2024 → disclosed May-2025) – 62.4 million U.S. & Canadian K-12 students + 9.5 million teachers. SSNs, medical & special-ed data stolen; ransom paid, but attackers still extort schools in July 2025.
- Bank Sepah, Iran (Mar-2025) – 42 million customer dossiers (≈12 TB), including military-loan files; $42 million Bitcoin ransom demanded by “Codebreakers” gang.
- 23andMe (Apr-2025 settlement) – 7 million genetic/ancestry profiles scraped via credential-stuffing; firm agrees to a $30 million compensation fund.
- UNFI / Whole Foods supplier (Jun-2025) – Cyber-attack knocks out North-American grocery ordering for a week, spotlighting food-supply-chain risk.
- NationsBenefits (Apr-2025) – 3 million U.S. health-plan members; PHI stolen in Clop ransomware via GoAnywhere MFT flaw.
Financial snapshot (2025)
- Average direct cost for a 50-employee e-commerce shop: $120k-$180k (forensics, card-reissue, fines).
- 42% of breached retailers lost more than 10% of annual revenue to customer churn within 12 months.
Reputational Damage:
Trust, once lost, is incredibly difficult to regain. A data breach signals to customers that a brand is not a reliable custodian of their information, leading to a direct and often permanent loss of loyalty.
Legal Consequences:
Non-compliance with data protection regulations carries severe penalties. Under GDPR, fines can be astronomical, as demonstrated by the €1.2 billion fine levied against Meta in 2023. Businesses also face the high probability of class-action lawsuits from affected customers.
Common Types of E-commerce Data Breaches
Attackers employ a variety of methods to compromise online stores. Understanding these vectors is the first step toward building an effective defence.
1. Phishing and Credential Stuffing: Phishing attacks utilise deceptive emails to trick employees into revealing login credentials. Attackers then exploit these credentials or lists stolen from other breaches to gain unauthorised access. Notably, 40% of malware attacks are initiated via email links.
2. Payment Card Fraud (E-skimming): This is one of the most direct threats to e-commerce. Attackers inject malicious code (e.g., Magecart malware) onto checkout pages to steal payment card data in real-time as customers type it.
3. SQL Injection (SQLi) and Cross-Site Scripting (XSS)
These attacks exploit vulnerabilities in a website’s code:
- SQL Injection (SQLi): Manipulates the database by inserting malicious queries.
- Cross-Site Scripting (XSS): Executes harmful scripts in a user’s browser.
They are a critical concern for platforms like WordPress and Magento.
4. API Abuse: As e-commerce platforms increasingly rely on interconnected services, poorly secured Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) become prime targets for attackers. Attackers abuse these APIs to gain unauthorised access to sensitive data and functionality.
5. Ransomware: Ransomware attacks involve encrypting a business’s critical data and demanding a ransom for its release, leading to massive operational disruption. In 2022, 36.4% of enterprises reported impacts from third-party system compromises related to ransomware.
6. Insider Threats
Not all breaches originate externally. Insider threats can stem from:
- Employee errors (e.g., accidental data exposure)
- Malicious insiders (e.g., disgruntled employees deliberately leaking or misusing data).
Risk Assessment and Detection Strategies
Proactive monitoring and regular security assessments are crucial for identifying vulnerabilities before they can be exploited.
Penetration testing and security audits
Determining vulnerabilities before attackers can capitalize on them requires regularly planned penetration tests and security audits. Ethical hackers perform penetration testing to simulate an attack to recognise issues such as outdated software patches on platforms like Magento or improperly configured security settings.
Warning Signs for Device and Account Monitoring
One important sign of possible compromise is suspicious account activity. This includes login attempts from odd geographic locations or several unsuccessful attempts from a single IP address. Another issue is unusual traffic spikes, which could indicate a bot-driven credential stuffing attempt or a distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attack.
Tools for Threat Detection
Consequently, Security Information and Event Management ( SIEM ) systems aggregate and analyse log data from across the infrastructure and provide real-time alerts for suspicious activity. Hence, an Intrusion Detection and Prevention System ( IDS/IPS ) monitoring device electronically monitors network traffic for known attack patterns and can automatically block malicious activity. Moreover, behavioural analytics solutions establish a baseline of normal user and administrator behaviour and generate alerts when deviations occur that may indicate a compromise.
Importance of Continuous Monitoring
Early cyber threat detection requires constant monitoring. According to research, it takes an average of 207 days to detect a breach, providing attackers sufficient time to inflict significant harm. One of the main objectives of any security programme should be to decrease this dwell time.
Proactive Monitoring:
Furthermore, continuous monitoring is key to early signal detection. 65% of the organisations reported by IBM stated they were still dealing with the data breach. The average time to detect a breach is 207 days in 2022, a window that gives attackers ample time to cause significant damage [IBM Report]. But 35% indicated they had fully healed, which is almost three times the number from the previous year (12%). This improvement happened simultaneously with the lowest rate of quickly finding and fixing breaches in nine years. Nonetheless, reducing this dwell clock time is a principal goal of any security computer programme.
Comprehensive e-commerce Security Checklist
A layered, defence-in-depth strategy is the most effective way to protect an online store.
Secure Website Infrastructure
- Use SSL/HTTPS encryption: Encrypt all data that is sent between your customers and your server. SSL is used by 86.1% of websites as a standard practice.
- Harden Hosting: Selecting a secure web host with features such as DDoS protection, firewalls, and two-factor authentication (2FA), which you must use to access your account.
- Set up a Web Application Firewall (WAF): A WAF is a crucial shield that stops bad traffic, such as SQL injection and XSS attacks, from reaching your application.
Authentication and Access Controls
- Enforce Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Require MFA for all administrative users and offer it as a course of action for customers to safeguard their accounts.
- Use Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Adhere to the Principle of Least Privilege, granting employees access only to the data and systems necessary for their jobs.
- Implement Strong Password Policies: Enforce complexity requirements for passwords and cap the number of failed login attempts to thwart brute-force attacks.
Software and Plugin Maintenance
- Keep Everything Updated: Regularly update your CMS (e.g., Magento, Shopify, WooCommerce), themes, and plugins to the latest versions.
- Automate Patch Management: Apply tools to automate the application of security patches, ensuring vulnerabilities are fixed as soon as a solution becomes available.
Secure Payment Processing
- Achieve PCI DSS Compliance: Adhere to the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS), which is mandatory for handling card data.
- Use Tokenisation: Partner with a payment gateway that uses tokenisation. This ensures sensitive cardholder data never touches your servers, dramatically reducing your risk and compliance burden.
- Deploy Fraud Detection Tools: Apply standard checks such as Address Verification System (AVS) and Card Verification Value (CVV) to help prevent fraudulent transactions.
Data Protection and Storage
- Encrypt Data at Rest: Encrypt sensitive data stored in your database and on your server.
- Avoid Storing Cardholder Data: Never store full credit card numbers. Rely on secure, compliant payment gateways like PayPal and Stripe.
- Implement Secure Backups: Regularly back up your data to a secure, access-restricted cloud environment.
Monitoring and Threat Detection
- Enable Real-Time Monitoring: Use IDS/IPS and SIEM tools to monitor your systems for signs of an attack.
- Track Unusual Activity: Set up alerts for repeated failed login attempts, large data transfers, or access from suspicious IP ranges.
Employee Training and Insider Threat Mitigation
- Conduct Regular Cybersecurity Training: Educate employees on how to recognise phishing attempts and follow security best practices to prevent human error.
- Limit and Audit Admin Privileges: Access to sensitive systems should be restricted, and the activity of privileged accounts should be audited regularly.
Customer Privacy and Trust
- Maintain a Transparent Privacy Policy: Clearly communicate what data you collect and how you use it, ensuring compliance with regulations such as GDPR and CCPA.
- Offer Consent Management: Give customers clear control over their data and how it is used.
- Educate Customers: Encourage customers to use strong, unique passwords and be aware of phishing risks targeting them.
Advanced Security Measures
Organisations aiming for a more mature security posture can implement several advanced measures to enhance their protection. By using ethical hackers to actively try to penetrate defences and find intricate weaknesses, penetration testing and red teaming go beyond automated scanning. A bug bounty program incentivises the global security research community to identify and responsibly report flaws in systems in exchange for remuneration.
AI-based fraud detection utilises machine learning algorithms to analyse transaction patterns in real-time, identifying and preventing sophisticated fraud attempts that rule-based systems may miss. Zero Trust architecture employs a “never trust, always verify” security model, positing that threats can originate from within or outside the network. As a result, each person and device requesting access must undergo rigorous verification.
Regulatory and Compliance Considerations
Navigating the legal landscape of data protection is a critical component of e-commerce cybersecurity. Data privacy and security are governed by a complex web of laws and regulations, each with a specific scope and purpose.
PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard)
The PCI DSS is a mandatory, prescriptive framework for businesses handling payment card data. It was established by the major payment card brands (like Visa, Mastercard, and American Express) to reduce credit card fraud. Compliance with PCI DSS involves a set of 12 requirements, which include building and maintaining a secure network, protecting cardholder data, and regularly testing and monitoring networks. Failure to comply can result in fines and the loss of the ability to process card payments.
GDPR and CCPA
These are landmark privacy laws that give individuals greater control over their personal data.
- GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation): This is a European Union law that protects the data and privacy of all EU residents. It requires organisations, regardless of location, to obtain explicit consent for data collection and to provide timely notifications of data breaches. GDPR grants individuals several rights, including the right to access, rectify, and erase their data. Fines for non-compliance can be substantial.
- CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act): The CCPA is a state law in the U.S. that protects the personal information of California residents. Similar to GDPR in its intent to provide data transparency and control, it has key differences, such as focusing on an “opt-out” mechanism for data sharing, as opposed to GDPR’s “opt-in” consent requirement.
U.S. State Laws
In the U.S., each state has specific laws governing how private companies must notify individuals about data breaches involving their personal information. These state-specific requirements exist in addition to federal laws and broader state-level regulations such as the CCPA. Every state’s law outlines unique stipulations for these notifications.
- Who must be notified (individuals, state attorney general, or consumer reporting agencies).
- What constitutes a breach and the type of data that triggers the notification requirement.
- When and how the notification must be delivered.
Compliance Benefits:
Adhering to these regulations is not just about avoiding massive fines and lawsuits; it is a powerful way to demonstrate a commitment to customer privacy and build brand trust.
Practical Steps:
To ensure compliance, businesses should
- Map data flows.
- Document compliance processes.
- Consult legal experts, especially for multi-jurisdictional operations.
Incident Response and Recovery Plan
No defence is infallible. A well-prepared business must have a plan for what to do when a breach occurs.

Breach Response Steps:
- Detection and Containment: Priority is to quickly identify the breach and isolate the affected systems to prevent further damage.
- Communication: Transparently notify customers, key stakeholders, and regulatory bodies as required by law. Pre-drafted communication templates help save critical time.
- Regulatory Reporting: Comply with all legal requirements for reporting breaches to authorities under regulations like GDPR and state laws.
- Post-Breach Audit: A comprehensive forensic investigation is essential to pinpoint the root cause of the breach and implement the necessary corrective measures to prevent future occurrences.
- Disaster Recovery Plan: Activate your disaster recovery plan, which should include processes for restoring data from secure backups and ensuring business continuity.
- Customer Support: Mitigate the harm to customers by offering services like free credit monitoring or identity theft protection.
Continuous Security Improvement
Cybersecurity is not a one-time project but an ongoing process of adaptation and improvement.
- Track KPIs: Monitor key performance indicators such as the time to detect a breach, patch compliance rates, and customer trust scores to measure the effectiveness of your security programme.
- Regular Assessments: Schedule recurring vulnerability scans and security audits to ensure your defences remain strong.
- Stay Updated: Leverage threat intelligence from industry reports, security conferences, and government alerts to stay informed about the latest attack techniques.
- Evolve Your Defences: Continuously update your security posture to counter emerging risks, such as sophisticated AI-driven phishing attacks.
Conclusion
Protecting an e-commerce site from a data breach requires a multi-layered approach. This strategy must combine robust technology ( such as encryption, WAFs, and SIEM), heightened human awareness (through employee training and customer education), and strict adherence to compliance mandates. In the modern digital economy, ongoing vigilance is not optional; it is the price of doing business and the foundation of customer trust.
Call to Action: Do not wait for a breach to happen. Audit your e-commerce site’s security today using the checklist in this guide, and consult with cybersecurity experts to develop tailored solutions that protect your business and your customers.
FAQ’s
An e-commerce data breach is the unauthorized access to sensitive customer or business data. It is dangerous because it leads to direct financial loss, severe reputational damage, and significant legal penalties.
Look for signs like unusual account activity, unexplained traffic spikes, or reports of unauthorized transactions. Use security tools such as SIEM and IDS for proactive detection.
The most common attacks include phishing, credential stuffing, SQL injection, XSS, and e-skimming (often using Magecart malware) that target checkout pages.
PCI DSS provides a strict framework of controls designed to protect payment data. Compliance ensures you are implementing essential security measures such as encryption, access controls, and regular network audits.
Immediately work to contain the breach by isolating affected systems. Then, begin the process of notifying affected parties and reporting to regulators while conducting a comprehensive forensic audit to understand the root cause.
Teaching customers to use strong, unique passwords and to recognize phishing attempts makes them less vulnerable to account takeover attacks, strengthening the overall security of your platform.
A disaster recovery plan ensures you can quickly restore your data and operations after an incident, minimizing costly downtime and reducing the overall financial impact of a breach.




